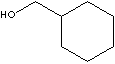
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
MELTING POINT
SOLUBILITY IN WATER
AUTOIGNITION
NFPA RATINGS
REFRACTIVE INDEX
FLASH POINT
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS
Alcohols are widely used as solvents, fuels and chemical raw materials. Generally, hydroxyl group compounds are polar, which trends to promote solubility in water. But the carbon chain resist to solubility in water. Short chain alcohols (methanol, ethanol, and propanol) in which the hydroxyl group predominates are miscible in water. Butanol is moderately soluble because of the balance between the two opposing solubility trends. Higher alcohols are practically insoluble in water because of the hydrocarbon chain's trend is stronger. Alcohols are "protic" solvents. Protic refers to a hydrogen atom attached to an electronegative atom, oxygen. Polar protic solvents are compounds that can be represented by the general formula ROH of which water (H2O), methanol (CH3OH) and acetic acid (CH3COOH) are examples. Water-soluble alcohols, low-molecular weight products, are solvents for the manufacture of coatings, dyes and inks, plastics, flavorings, personal-care products, pharmaceuticals, and cleaners. The higher alcohols, slightly soluble in water or insoluble, can provide the proper balance of target properties when solvent-based solvents are formulated for desired viscosity, flowing and leveling, and curing rate and can be used as coupling agents in waterborne coatings.
Alcohols are very weak acids as they lose H+ in the hydroxyl group. Alcohols undergoes dehydration reaction which means the elimination of water molecule replaced by a pi bond between two adjacent carbon atoms to form alkenes under heating in the presence of strong acids like hydrocloric acid or phosphoric acid. Primary and secondary alcohols can be oxidized to aldehydes and ketones respectively. Carboxylic acids are obtained from oxidation of aldehydes. Oxidation in organic chemistry can be considered to be the loss of hydrogen or gain of oxygen and reduction to gain hydrogen or loss of oxygen. Tertiary alcohols do not react to give oxidation products as they have no H attached to the alcohol carbon. Alcohols undergoes important reactions called nucleophilic substitution in which an electron donor replaces a leaving group, generally conjugate bases of strong acids, as a covalent substitute of some atom. One of important reaction of alcohol is condensation. Ethers are formed by the condensation of two alcohols by heating with sulfuric acid; the reaction is one of dehydration. Almost infinite esters are formed through condensation reaction called esterification between carboxylic acid and alcohol, which produces water. Alcohols are important solvents and chemical raw materials. Alcohols are intermediates for the production of target compounds, such as pharmaceuticals, veterinary medicines, plasticizers, surfactants, lubricants, ore floatation agents, pesticides, hydraulic fluids, and detergents.
Carbinol is a primary alcohol with general formula RCH2OH. In carbinol nomenclature system, the term of carbinol is methanol itself and other groups are considered to have replaced one of the methanol hydrogen atoms to describe larger alcohols as derivatives of carbinol. This nomenclature system is particularly useful when the groups attached to the methanol carbon are large, aromatic, and cyclo groups. Benzyl alcohol is called phenylcarbinol or benzenecarbinol while benzyl carbinol is phenylethyl alcohol.
APPEARANCE
98.0% min
Hazard Symbols: , Risk Phrases: , Safety Phrases: 23-24/25
Cyclohexane is the six-membered alicyclic hydrocarbon consisting of six carbon atoms linked to each other to form a ring, with each carbon atom bearing two hydrogen atoms, C6H12. A cyclic compound is an organic compound that contains one or more closed rings of carbon atoms. The term alicyclic refers to cyclic compound that behaves chemically like aliphatic compounds (open-chain), which means the exclusion of carbocyclic compounds of aromatic rings with an array of π-electrons characteristic. Cyclohexane is a colorless, highly flammable, mobile liquid with a pungent odor. It is insoluble in water and soluble in alcohol, ether, and almost organic solvents. Cyclohexane is a non-corrosive and quick volatilize liquid and sublimes between -5 to 5 C. Cyclohexane can exist in a number of interconvertible three-dimensional conformations, the two simplest being are the chair and boat conformation and others include the half-chair and twist-chair conformation. Cyclohexane can cause irritation to the eyes and mucous membranes in workers. Repeated and prolonged contact with skin may cause dermatitis. The substance has not been shown to cause the hematologic changes associated with exposure to benzene. Cyclohexane occurs naturally in crude oils. Some cyclohexane is recovered from petroleum streams by fractionation. The bulky commercial production of cyclohexane is based on hydrogenation of benzene in closed system. Cyclohexane consumption is linked almost entirely to nylon production. Nylon is further processed into fibers for applications in carpeting, automobile tire cord, clothing, and other growing industrial fields. Cyclohexane is used as a solvent, oil extractant, paint and varnish remover, dry cleaning material, and in solid fuels. It has been used as a insecticide itself. Cyclohexane is used as a chemical intermediate to produce target molecules. Natural compounds of one to five alicyclic rings with great variety and complexity are found particularly in steroids and terpenes. Cyclohexane structure, six membered-ring, is one of the major skeleton in nature. Cyclohexane derivatives can be used for the synthesis of pharmaceuticals, dyes, herbicides, plant growth regulator, plasticizers, rubber chemicals, cycloamines and other organic compounds.